Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a hard and chemically resistant oxide of titanium. Using TiO2 sputtering target can obtain good quality titanium dioxide films, which have been widely used in various applications due to their multiple interesting properties. The first half of this passage introduces some of the properties and applications of titanium oxide film, and the latter part focuses on studies on TiO2 film deposition rate.
Titanium Dioxide Film Properties
| Material Type | Titanium (IV) Oxide |
| Symbol | TiO2 |
| Color/Appearance | White-Beige, Gray-Black |
| Theoretical Density | 4.23 g/cc |
| Melting Point | 1,830 °C |
| Sputter | RF, RF-R |
| Type of Bond | Indium, Elastomer |
| Comments | Suboxide, must be reoxidized to rutile. Ta reduces TiO2 to TiO and Ti. |
| Available Sizes | Dia.: 1.0″, 2.0″, 3.0″, 4.0″, 5.0″, 6.0″ Thick: 0.125″, 0.250″ |
Titanium Dioxide Film Applications
* Thin Film Deposition:
Titanium oxide TiO2 sputtering target is used for thin film deposition, typically for fuel cell, decoration, semiconductor, display, LED and photovoltaic devices, glass coating, etc.
* Paints and Coatings:
Titanium dioxide film provides opacity and durability, while helping to ensure the longevity of the paint and protection of the painted surface. TiO2 film has a high refractive index, which makes it attractive for the glass coating industry to produce low emissivity and antireflective coatings.
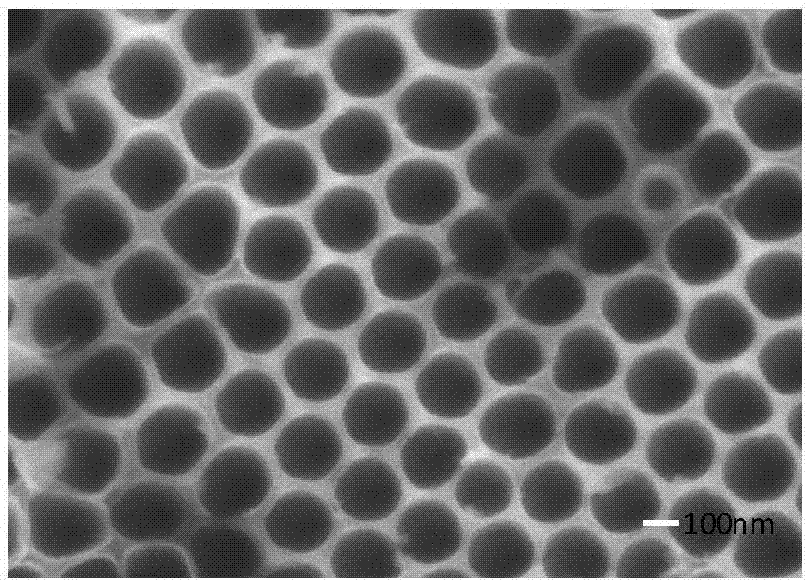
* Plastics, Adhesives and Rubber:
Titanium dioxide can help minimize the brittleness, fading and cracking that can occur in plastics and other materials as a result of light exposure.
* Cosmetics:
Pigment-grade titanium dioxide is used in some cosmetics to aid in hiding blemishes and brightening the skin. Titanium dioxide allows for the use of thinner coatings of make-up material for the same desired effect. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891.
* Paper:
Titanium dioxide is used to coat paper, making it whiter, brighter and more opaque.
* Food Contact Materials and Ingredients:
The opacity to visible and ultraviolet light offered by titanium dioxide protects food, beverages, supplements and pharmaceuticals from premature degradation, enhancing the longevity of the product. Specific classes of high purity pigment-grade titanium dioxide are also used in drug tablets, capsule coatings and as a decorative aid in some foods.
Titanium Dioxide Film Synthesis
Although many deposition techniques can be used to synthesize titanium dioxide film, magnetron sputtering is still the preferred method for large area coatings. This is due to its versatility, uniformity, ease of expansion and high throughput of magnetron sputtering. However, its inherent instability indicated by hysteresis effect limits the achievable composition or substantially reduces the deposition rate. In general, closed loop control of the reaction gas pressure must be employed to achieve high deposition rates and optimum film properties.
Studies on Titanium Dioxide Film Deposition
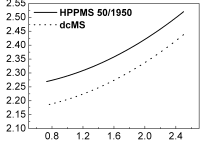
Recent studies have shown the use of titanium oxide (TiO1.8) sputtering targets to deposit titanium dioxide films. The main reason for using TiO1.8 sputtering target is its conductivity makes DC sputtering possible. This sputtering method has a significantly higher deposition rate and no hysteresis compared to a metal target operating in a composite mode in magnetron sputtering.
Results of the study show that the high deposition rate is related to the presence of lower Ti oxides (suboxides) at the target surface. The deposition rate of stoichiometric TiO2 from the suboxide target is about five times higher than the metal target operating in the compound mode. The rate of growth from 100% to 65% of the sputtering target is less than expected, only increasing by about 10%. The result is strongly influenced by the residual atmosphere. This is primarily due to the low deposition rate due to the small target size and low power density.
In conclusion, the result shows that by adjusting the O/Ti ratio of the target (to achieve low Ti oxide), we can increase the deposition rate of titanium dioxide film. This result is significant for the application of titanium dioxide as it increases the throughput of the coating process.
Thanks for reading this passage and hope that you now have a basic understanding about titanium dioxide film. Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a leading sputtering target manufacturer based in Lake Forest, California. If you feel interested about the TiO2 sputtering targets, you can go to our product page for more information, or directly send us an inquiry. You can also contact us via target@samaterials.com. Free samples are available.



