What is Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)?
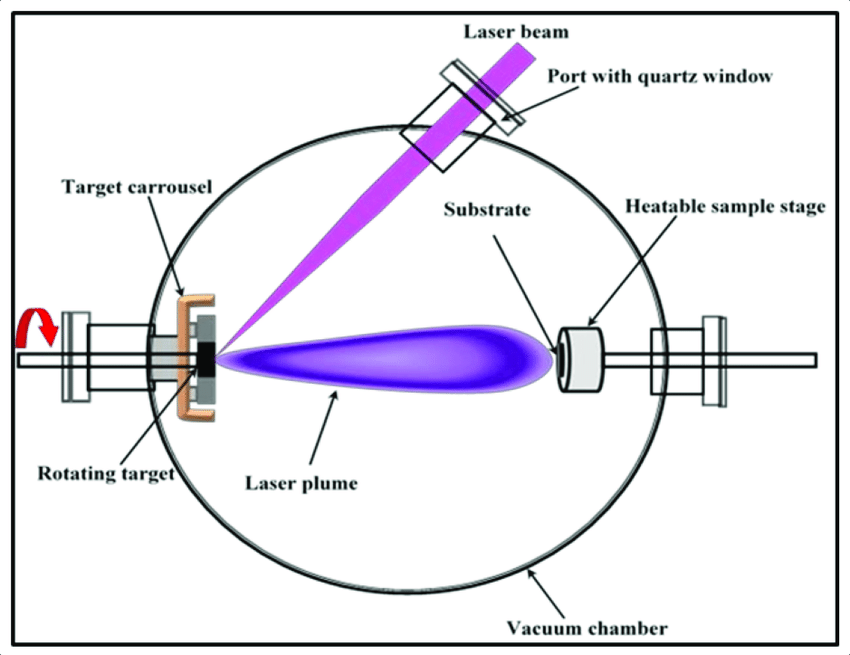
Pulse laser deposition is a method of physical vapor deposition. In this process, a high-power pulsed laser beam is centered on a target within the vacuum chamber. The laser beam vaporizes the target material and deposits it as a thin film on a substrate. The process involves evaporation, ablation, plasma formation, and exfoliation.
In 1965, Smith and Turner carried out the first pulsed-laser deposition using a ruby laser. However, the quality of objects produced by this process was inferior to those produced by other methods of thin-film deposition. The big break for PLD came in 1987 when D. Dikkamp, Xindi Wu, and T. Venkatesan deposited a thin film of Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide on a high-temperature semiconductor using laser deposition. The product they got had a superior quality to those gotten from other methods of thin-film deposition.
Factors that Affect PLD Deposition Rate
Five major factors affect the deposition rate when using pulsed laser deposition.
Target Material
The target material is one important factor that affects the deposition rate. The thickness and melting point of the target material influence the deposition rate. Target materials with less thickness and a low melting point have a higher deposition rate.
Laser Pulse Energy
The greater the laser pulse energy, the faster the deposition rate of the process.
Repetition Rate of the Laser
With all factors being equal, a higher laser repetition rate translates to a higher deposition rate.
The Temperature of the Substrate
When the substrate has a high temperature, the rate of deposition increases.
Distance between Target and Substrate
The distance between the target and substrate has a huge impact on the deposition rate. The greater the distance between the target and the substrate, the greater the deposition rate.
Type of Gas
To a large extent, the type of gas determines the pressure in the chamber. Higher pressure in the chamber leads to a lower deposition rate.
Advantages of Pulsed Laser Deposition
Pulsed laser deposition is a popular choice for thin-film deposition due to its numerous advantages. These advantages include:
Easy Concept
Pulsed laser deposition is an easy concept to grasp. The process simply requires focusing a laser beam on a target material to vaporize the material and deposit it on a substrate.
Uniformity
Products coated with this method usually have uniform thin-film deposition compared to those coated with other methods.
Convenience
PLD is a rather convenient process. It can work with low temperatures. In addition, it is flexible and compatible with various target materials.
Precision
Pulsed laser deposition is a precise process. It functions with a high level of control.
Sustainability
This process does not pose any environmental threat nor does it require extremely high energy. It is a sustainable method of thin-film deposition.
Limitations of Pulsed Laser Deposition
Despite all the advantages of pulsed laser deposition, it has some limitations that are still being worked on. Its limitations are as follows:
Slow Rate of Deposition
The average rate of deposition in PLD is slow. Therefore, it is less ideal for coating substrates with a large surface area than other methods.
Cost
Pulsed laser deposition is quite expensive as a method of thin-film deposition. For this reason, it is most suitable for high-tech applications. It is not suitable for low-tech applications because there are less costly alternatives.
Quality
In some cases, there are particles of the target material on the deposited film. These particles do not give the substrate a neat finish, reducing the quality.
Conclusion
Pulsed laser deposition is an excellent method for producing thin films. Research is ongoing on ways to advance laser deposition technologies. This means that PLD will only become more popular in the future. For more information about metal manufacturing, please visit https://www.sputtertargets.net/.



