Metal casting is an industrial manufacturing process that is more than 5,000 years old. To date, it continues to play a critical role in the production of essential manufacturing components for the production of automobiles, aircraft, ships, heavy equipment, machining tools, and even plant machinery. In this post, you’ll discover what metal casting is, the process of metal casting, its advantages, and its applications.
What is Metal Casting?
Metal casting, or simply casting, is a material shaping method that involves the pouring of a liquid material (molten metal) into a mold that contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape. The casting is allowed to solidify and then removed from the mold to complete the casting process. Essentially, metal materials of different shapes and sizes are produced from casting. Metal casting is an important method to make titanium sputtering targets from metal titanium.
Casting is one of the oldest manufacturing processes known, and used to confer strength and rigidity to intricate parts. The mold used in the casting process is usually made of heat-resisting material. A major component of this material is sand; it is mostly used because it is capable of resisting the high temperature of molten metal. Permanent molds of metal can also be used to cast products.
How is Metal Casting Processed?
The metal casting process is in 5 successive stages.
Patternmaking
In the first stage, a replica of the exterior of the casting is made. This replica is the desired pattern, which can be made of clay, wood, metal, plastic, or plaster. In industrial part-making, patternmaking is a very important process that involves the use of precise calculations to make pieces fit and work together.
Core-making
The next stage is core-making. This is required for hollow casting. An additional piece of clay, sand or metal, known as the core, helps to shape the internal form of the casting to make it hollow. Cores are made to be strong but also collapsible, making them easy to remove from the finished casting.
Molding
The molding process involves the forming of a cast around the pattern using a mold. It is usually a multi-step process where a mold is contained in a frame called a flask. Usually, green sand or molding sand is packed into the flask around the pattern, a process known as metal sand casting. If the sand is packed correctly, the cast will remain after the material has been removed.
Another method around this is that a two-piece, non-destructible metal mold is created. This approach allows for a separate and repeat use of the mold for the casting of other identical parts for industrial applications.
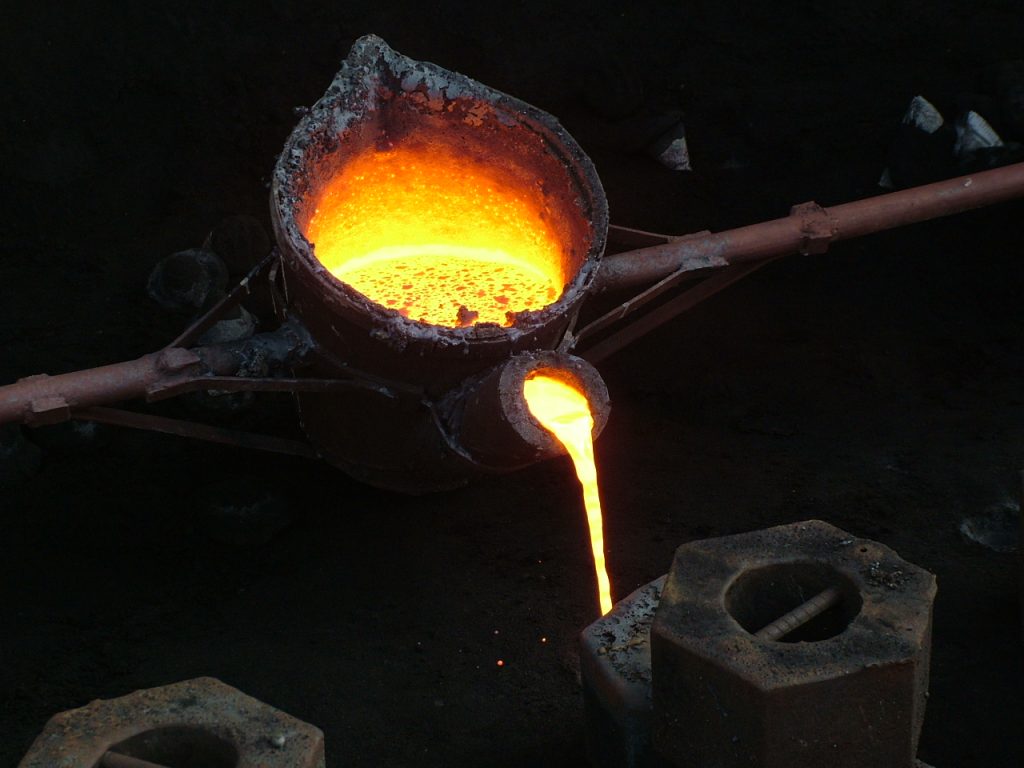
Melting and Pouring of Molten Metal
This step is simple, yet very important. The metal material for the casting is melted to produce molten metal, which is then carefully poured into the cavity of the mold and left to fir solidify. After the solidification of the cast, the new material is removed, a process known as the shakeout process. The mold is subjected to vigorous vibration or shaking to remove sand from the casting. In industrial processes, special shakeout equipment is employed to ensure high production output due to its efficient and smooth performance.
Sand is removed and collected, cooled, and reclaimed for future use in other casting processes. Manufacturers also have special equipment that helps to make the process of sand separation from castings pretty seamless and fast. These machines help to remove and cool the sand and castings, as well as moisture. They also help to drastically minimize casting damage, which is typical at this stage in the casting process. At the end of the day, what we have are two products, namely: a clean cast and sand, which are ready for the reclamation process.
Cleaning
This is the final step, where the cast metal product is finally ejected from the mold and then fettled. Fettling involves the cleaning of the object and removal of any molding material and rough edges.
Other types of casting include centrifugal casting, permanent mold casting, plaster casting, sand casting, and investment casting.
Advantages of Casting
Metal casting is used extensively in manufacturing because of these advantages:
- It allows for the making of intricate shapes since molten material can flow into very small sections. This eliminates the need for other operations like machining, forging, and welding.
- The process allows for the casting of any material that is ferrous or non-ferrous.
- It supports large savings in weight, as the metal can be placed exactly where it is needed.
- The tools required for casting molds are simple to use and relatively inexpensive.
- The casting process is not limited by the size and weight of the product.
- Metal casting is the only method for producing certain parts made from metals and alloys.

Applications of Metal Casting
Castings are used virtually in every industrial manufacturing process where. Amongst all, automobile and heavy equipment manufacturing is the predominant sector, taking up more than 50 percent of castings applications.
Below is a sector-by-sector application of metal casting:
- Transport: This includes automobile manufacturing, the aerospace industry, railways, and shipping.
- Heavy Equipment: Notable applications include farming, construction, and mining.
- Industrial Machine Tools: Casting is commonly used in making machining materials, plastics molding, forging, extrusion, and forming.
- Electrical Equipment Machines: It is used for making electrical motors, pumps, and generators.
- Plant Machinery: Casting is also applicable in chemical, petroleum, paper, sugar, textile, steel, and thermal plants
- Defense Equipment: Casting finds application in military vehicles, artillery, and munitions.
- Household Appliances: Kitchen cutlery, gardening equipment, and some furniture.
- Hardware: Casting is used to make pipes for the plumbing industry, as well as joints, valves, and fittings.
- Art Objects: Casting plays a critical role in making sculptures and several decorative items.
Other Metal Manufacturing Process
Casting is just one of the several metal manufacturing processes, which also include turning, powder metallurgy, drilling, milling, shaping, planing, broaching, machining, and sawing.
Conclusion
Metal casting is an industrial manufacturing process that is used extensively in several manufacturing processes, with the transportation and heavy equipment industries taking up a larger percentage of the product. It is also used in the manufacture of aircraft, ships, heavy equipment, machining tools, art objects, and many more applications. For more information about metal manufacturing, please visit https://www.sputtertargets.net/.



